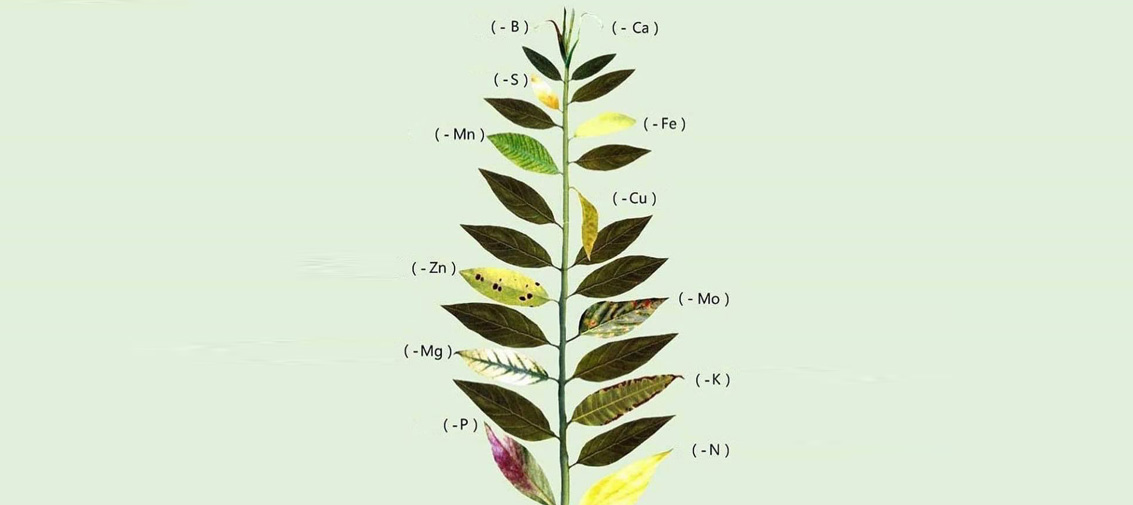
Micronutrients Deficiency Chart
The most common symptoms of nutrient deficiency are stunted growth and leaf discoloration. The position of the symptoms (distal, basal or intermediate) depends on the mobility of the nutrient inside the plant (young leaves competing with oldest leaves).
ON TERMINAL BUDS: Ca & B
(CA) Calcium: Plant dark green. Tender leaves pale. Drying starts from the tips. Eventually leaf bunds die.
(B) Boron: Discoloration of leaf buds. Breaking and dropping of buds.
ON YOUNG LEAVES: Cu. S, Fe & Mn
(Cu) Copper: Pale pink between the veins. Wilt and drop.
(Mn) Manganese: Leaves pale in color. Veins and venules dark green and reticulated.
(S) Sulphur: Leaves light green. Veins pale green. No spots.
(Fe) Iron: Leaves pale. No spots. Major veins green.
ON OLD LEAVES: N, P, K, Mg, Zn & Mo
(N) Nitrogen: Stunted growth. Extremely pale color. Upright leaves with light green/yellowish. Appear burnt in extreme deficiency.”
(P) Phosphorus: Plant short and dark green. In extreme deficiencies turn brown or black. Bronze colour under the leaf.
(K) Potassium: Small spots on the tips, edges of pale leaves. Spots turn rusty. Folds at tips.
(Mg) Magnesium: Paleness from leaf edges. No spots. Edges have cup shaped folds. Leaves die and drop in extreme deficiency.
(Z) Zinc: Leaves pale, narrow and short. Veins dark green. Dark spots on leaves and edges.
(Mo) Molybdenum: Leaves light green/lemon yellow/orange. Spots on whole leaf except veins. Sticky secretions from under the leaf.
THE COLOURS REPRESENTED ARE INDICATIVE THEY MAY VARY FROM PLANT TO PLANT